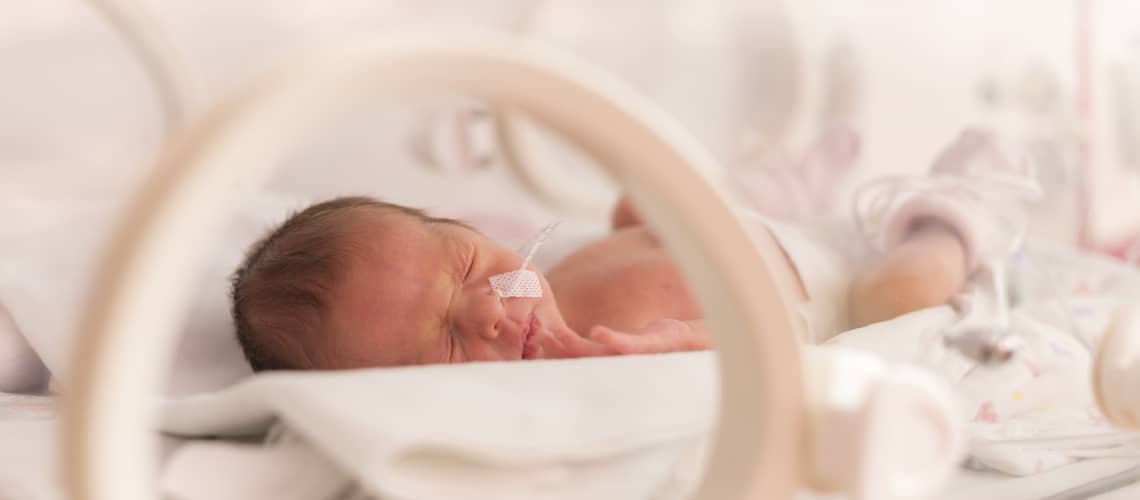
Premature babies. Premature birth at 25 weeks can have consequences
The issue of premature babies is very complex. World medicine itself (pediatrics, neonatology) is still coming up with new knowledge and findings in this area. These are related to the reasons and causes of premature births, the development of premature babies, care and the consequences that premature birth can have on children. The number of premature babies continues to rise. For parents-to-be, premature birth can be shocking, stressful and full of anxiety. This is because it is a condition that is considered risky and, moreover, it is a very sensitive topic. When is a baby full-term and when is it considered premature? How do premature babies develop?
Prematurely born children or premature women within the birth rate record an ever- increasing increase. On average, up to 15 million babies are born prematurely every year. In this case, mortality is still a big risk - the death of premature babies or other long-term consequences. It is a statistical fact that thanks to new technologies, a lot of new knowledge and higher expertise of doctors, it is possible to successfully save the lives of premature newborns worldwide. What does it mean if a baby is born prematurely? What is a gestational week in pregnancy?
Premature child - premature baby
The World Health Organization (WHO) considers any newborn born before the 37th week of gestation to be premature. Gestational age is the age of the baby - the fetus that has reached maturity in the womb (womb). It is counted from the first day of the end of regular menstruation. The greatest risk is premature birth from the point of view of the risk of death of premature babies or the emergence of permanent consequences. The child is fully termed in the 40th gestational week.
It is true that the lower the gestational week, the higher the risk of complications for a premature baby. The shorter the pregnancy, the less mature the baby is. Since the baby has not yet matured enough in the womb, it requires special care. The largest group of premature babies are newborns born in the 34th to 36th gestational week. It is a group easily, or borderline immature newborns, who usually reach the weight of full-term babies, but nevertheless premature birth can cause several complications. The condition of newborns can be assessed based on gestational age as follows:
- slightly or marginally immature – 32nd – 36th gestational week,
- very immature – 28th – 31st gestational week,
- extremely immature - before the 28th gestational week.
A positive development in medicine, and especially in neonatology, is that while in the 90s a fetus weighing less than 1,000 g before the end of the 30th gestational week was considered unviable, today this limit has moved up to the 24th gestational week and the weight fruit over 500 g. In some countries, it is even possible to push this limit even lower, which contributes to saving even extremely immature children.
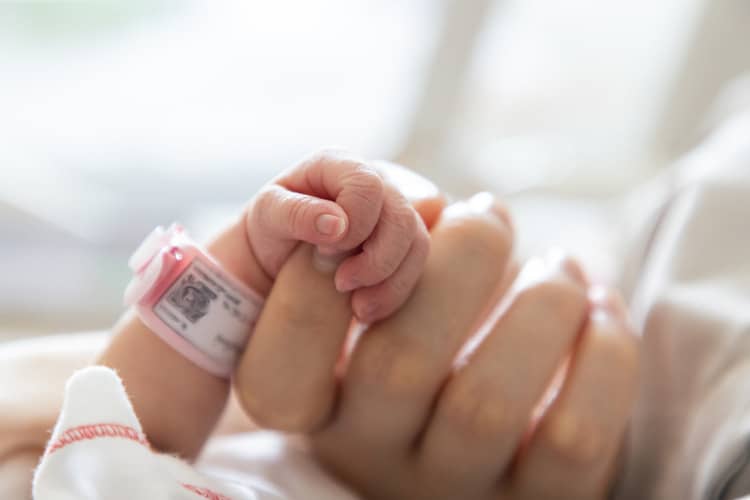

Premature babies at 28 weeks and earlier
Gestational age, i.e. the age the baby reached in the womb, is very often decisive for the survival and subsequent complications of immature children. Precisely in relation to the shorter duration of pregnancy, the consequence of which are premature births, medicine is increasingly focusing on prognosticating children who are born before the 28th gestational week (extremely immature).
Premature babies are very thin during this period - often even bony, as their birth weight is usually extremely low, below 1 kg. Statistically, the weight of a newborn up to 2.5 kg is considered low, below the limit of 1.5 kg it is a very low weight of the baby. The lower the birth weight, the higher the risk of morbidity, complications or even mortality in newborns. Premature birth in the 25th week or even in the 24th week, or premature birth in the 6th month, represent a high risk for the newborn, related to the immaturity of all systems in the body. Such babies may be considered "fetal" or their birth weight is assessed as very extremely low (below 750 to 500 g).
They require immediate care, placement in an incubator and the creation of conditions that will allow them to achieve further development. It is necessary to monitor their vital functions 24 hours a day in order to monitor possible complications and to be able to react immediately. The biggest problem with premature babies is the immaturity of their organs. If their organs do not function properly, it can cause serious health complications, chronic burns or even death. Most often, these are problems with breathing, digestion, heart activity, fluctuations in blood pressure or problems with the immune system. Growth disorders and frequent infections also appear. They usually have neonatal jaundice, the course of which is more complicated and lasts longer. There is also a higher risk of retardation, cerebral palsy, hyperactivity or attention disorders in such premature babies.
Premature babies in the 36th week
Premature babies in the 35th week, or 32 to 36 gestational weeks are considered slightly or marginally immature. Such a premature birth in the 8th month, i.e. 32nd week, is considered borderline. This does not mean that increased care is not necessary in the case of such a deadline. Such a birth is still characterized as premature, therefore risky. However, it is more likely that the child will spend significantly less time in the incubator and the risk of some health complications is lower than in the case of extremely immature or immature children. In such a case, the difference between the precocious child and his peers may not be so profound. Nevertheless, the care of a premature baby may still require more attention than it would be in the case of a regular due date. The rule still applies that the earlier a child is born, the higher the risk of health complications and permanent consequences.
Premature babies - development
In this case, a lot depends on the gestational age at which the baby was born, what its birth weight was, and what possible complications it encountered. It is therefore not possible to generalize the development of a premature child. Does a premature baby have any consequences? Do certain chronic problems persist? Are certain disorders or diseases diagnosed? All this can subsequently affect the further development of the premature baby.
Around the 3rd month, the baby's nervous and movement system matures. In the first months, problems with coordination or balance may occur. It is often a natural delay in neuromotor development. This may be related to the longer time it takes to learn to walk, but also to learn to speak. Incorrect development can also be related to asymmetry in the use of limbs - the child uses only one side of his body. A problem with coordination when moving the head or weakened muscles in the limbs may persist. A sign of improper development can be delayed movements or shaking of the limbs when crying. Many of the psychomotor deficiencies can disappear or diagnosis and appropriate therapy are needed, which can adjust the development in the right direction. Exercises and rehabilitation are key. If you notice certain abnormal factors, do not wait to see a pediatrician.
In development, long-term consequences can also appear, such as vision or hearing disorders. Attention deficits, hyperactivity or the development of epilepsy are quite typical. The prognosis of mental disability or the occurrence of cerebral palsy can also be serious. Usually up to 12 months, there is a constant risk that the premature baby will have lifelong consequences. Infections may occur more often, and the baby's weaker immunity is also a problem. Respiratory diseases (bronchopulmonary dysplasia) are common in infancy. Parents often worry about how quickly premature babies gain weight. Problems with nutrition and digestion, as well as more frequent infections and diseases, result in the baby not gaining weight as it should. Alternatively, what he gains, he quickly loses. However, in some premature babies, problems with weight gain may not be present and feeding is unproblematic.
Although some difficulties may appear in the course of the child's development, this does not mean that the premature child cannot lead a full life. If there were no more serious disorders, brain damage, diagnosis of mental or other disabilities that would have permanent consequences reducing the quality of his life, a premature child will catch up with his peers sooner or later.
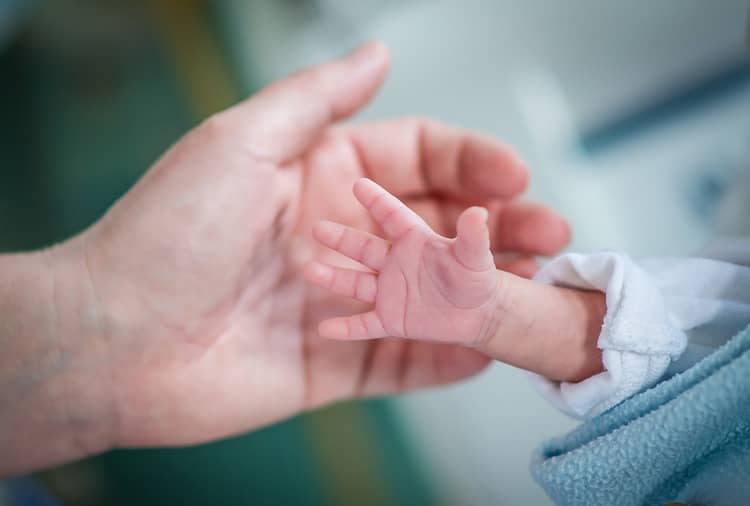

Caring for a premature baby
At the beginning of this paragraph, we would like to point out that the best thing to do is to consult your pediatrician regarding information on care, from creating a suitable environment to feeding, who will explain exactly how to proceed in the care of a premature baby in a specific case. You can also consult with the staff at the neonatology department, in case you receive the baby in home care. The requirements for care may differ for each premature child and it depends on the initial prognosis.
Parents must not despair, especially in the early days after the birth of the baby, although seeing their baby on the equipment in the incubator at the first moment may not be a pleasant sight (especially if it is an extremely immature premature baby). If possible, speak to the baby and communicate with him, your mutual contact is important. If it is later allowed by the doctors, apply the so-called kangarooing - the baby can be placed body on body and already here his connection with the parent is being built, which has a positive effect on further development. It stimulates his breathing and the child and parent are calmer.
Feeding a premature baby
Feeding will depend on the health status of the baby, but already in the beginning it will be necessary to pump breast milk, which should not be forgotten a few hours after birth. It will be necessary to vacuum several times a day (8 to 10 times). In the beginning, the baby will most likely be fed through a nasal or oral tube, or through a tube inserted into the stomach. Nutrition given to premature babies through the veins (intravenously) has also been proven. Later, the mother can be allowed to breastfeed, and even the minimum amount of breast milk that the baby receives from the breast is very positive. It is important that the baby develops a sucking and swallowing reflex. Premature babies are usually released from the maternity hospital only when they gain weight.
Premature babies are often more sleepy and have longer periods of sleep and do not always ask for breastfeeding. Watch how the baby gains weight. It is advisable to monitor the baby's stool and if breastfeeding is not sufficient, additional feeding will be necessary. The child should have a stool 2 to 5 times a day. It is advisable to start feeding premature babies at the age of 5-8 months from the date of their birth.
Later, the parents of a premature newborn must also take into account the fact that after returning from the hospital, it is necessary to continue the care to an increased extent. More regular visits to a pediatrician, neurologist, orthopedist, pulmonologist, hematologist, ophthalmologist, physiotherapist, and later maybe even a psychologist will be necessary. Prematurely born children are monitored more intensively until at least the 3rd year of life. Even after coming home, based on the prognosis, it is important to monitor the baby. In this direction, electronic babysitters with a camera and breath monitors are suitable.
Premature birth - causes and risk groups
Why do premature births actually occur? The causes of premature births are usually multifactorial. In the case of pregnant women, it is not always possible to find out why the premature birth occurred. However, it is clear that there are many reasons why children are born prematurely, while new accompanying factors appear regularly. Sometimes this condition is due to the riskiness of a given group of pregnant women, other times it is due to complications during pregnancy that affect the course of pregnancy. Here are some common reasons for premature births.
- Low maternal age (under 16 years) or high maternal age (over 37 years).
- Genetic factors leading to premature birth due to generational incidence.
- Excessive smoking and alcohol consumption.
- Regular strenuous or physically demanding activity.
- Bad social conditions for a pregnant woman.
- Absence of regular check-ups and examinations by a gynecologist.
- Women with chronic diseases – cardiovascular diseases, cardiovascular diseases, autoimmune diseases, kidney or respiratory diseases and others.
- Women who are expecting twins, triplets - multiple pregnancy
- Premature outflow of amniotic fluid.
- Occurrence of bleeding in pregnancy.
- Fetal defects or disorders.
- Hereditary - congenital defects of the uterus.
- Frequent infections of the urinary tract, fallopian tubes or birth canal.
- Placental insufficiency, when the placenta does not work properly.
- Incompetence of the cervix - premature opening.
- Women's psyche, sensitivity, anxiety, depression.
- Previous experience with premature birth.
One of the reasons may be the short period between two pregnancies, or non-compliance with the recommended birth interval and another pregnancy. Doctors also attribute a higher risk of premature birth to women who have had repeated miscarriages or suffer from diabetes. There is also an increased risk in women with obesity.

Premature birth - symptoms
If a woman has an increased risk of premature birth, it is possible to monitor certain warning signs. These can be a sign of delivery outside the expected term. Symptoms can be isolated or appear in various combinations, and again much depends on the course of pregnancy and the stage of preterm labor. How the baby behaves before birth can also be very specific.
- Abdominal hardening at regular intervals (contractions) and shortening of the interval between contractions.
- Nervousness, restlessness and a feeling of discomfort.
- Painful sensations in the lower abdomen, which may resemble menstrual cramps.
- Low back pain and pressure in the pelvis.
- Watery vaginal discharge, staining and possible discoloration or light bleeding.
- Nausea, vomiting or diarrhea.
- Premature outflow of amniotic fluid.
In any case, it is important to keep calm and contact your gynecologist as soon as possible. Resting on the left side and increasing fluid intake can help. If the symptoms of premature labor are very intense and combined, the time between contractions is shortened and contractions are more intense, the uterus opens or there is a premature outflow of amniotic fluid, it is necessary to go to the hospital immediately.
Experiences
Unfortunately, many mothers have experience with premature babies. Children born prematurely need an incubator after birth, long-term observation and increased care is necessary, but this does not always mean that the child will have lifelong problems. As the mothers testified in the discussions, lower weight is not decisive, what is important is the developmental stage in which the child was born.
The most frequent questions - FAQ
The topic of premature birth is very sensitive, but at the same time increasingly frequent. The number of premature babies is increasing, and so are the reasons for which premature births are increasing. Do you have such an experience? Have you experienced premature birth? If you have experience with premature birth, we will be happy if you join the discussion and express your opinion on this issue. Your recommendations and practical experience can greatly help others who are interested in this topic.
In what week is she born by default?
What complications can premature babies have at 25 weeks?
How fast do premature babies gain weight?
Pridať komentár





