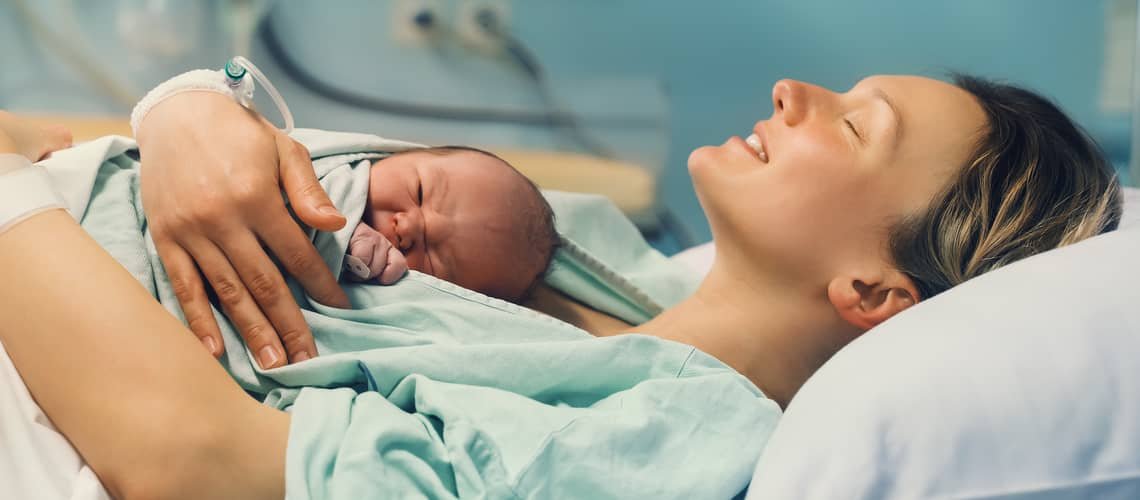
Bonding after childbirth and after caesarean section. Holding a newborn creates a bond
Childbirth is a very intimate matter for every woman. At the same time, it represents a specific experience that every woman experiences and describes differently. This special moment culminates in the birth of the baby. The term bonding is also related to the moments immediately after the birth of a newborn. In a simple translation from English, we can talk about connection or connection. The best expression of bonding in relation to childbirth is attachment. The first touches, the first contact between mother and newborn are an unrepeatable moment. In obstetric practice, bonding can be characterized as the first attachment of a newborn to the mother's belly or chest. This is skin-to-skin contact. It is implemented due to the creation of a strong emotional bond between mother and child.
The child was together with the mother for 9 months. All this time, the mother carried the child under her heart and looked forward to the moment when she would see what her child looked like, be able to touch him and look into his eyes. Immediate contact (skin to skin) of the child and the mother after birth, that's what bonding is. Bonding is proven to help, among other things, primarily build a strong emotional bond between the newborn and the mother. It is at this moment that the strongest relationship is created, the true love for the child. It is not only about the emotional relationship itself, this technique can be proven to have a positive effect on the physiological processes of the newborn. What is obstetric practice? How is bonding practiced in Slovakia? Is it appropriate to apply father bonding and is it possible to practice bonding after caesarean section?
What is bonding?
In obstetrics-neonatological terminology, bonding is an expression for the theory of the first contact of the mother with the child immediately after its birth. After birth, the newborn comes into the world where the mother is the most important element that connects him with the hitherto unknown environment. The essence of bonding is the creation of a bond between mother and child in a very sensitive and emotional period. During bonding, the baby is placed on the mother's stomach or to her breasts, and this is where their mutual emotional relationship is established. It is not only about the emotional nature of this bond.
Bonding – placing the newborn next to the mother skin-to-skin has a positive effect on the child's adaptation, building its immunity and proper thermoregulation. After birth, the newborn perceives the mother's scent, feels safe, and her breasts evoke the presence of amniotic fluid. The heartbeat, the mother's breathing and her smell are familiar stimuli for the child that evoke safety in him. If there are no postpartum complications or serious risks, bonding should be maximally supported by obstetricians. Bonding itself after birth is a process that affects not only the quality of the later relationship between the child and the parent, but also the social and psychological development of the child. The theory of bonding was developed by American pediatricians Marshall H. Klaus and John H. Kennell in the 1970s (its definition occurred in 1976). Today, the theory is enriched with practice and it is confirmed how important it is to build such an intimate bond.
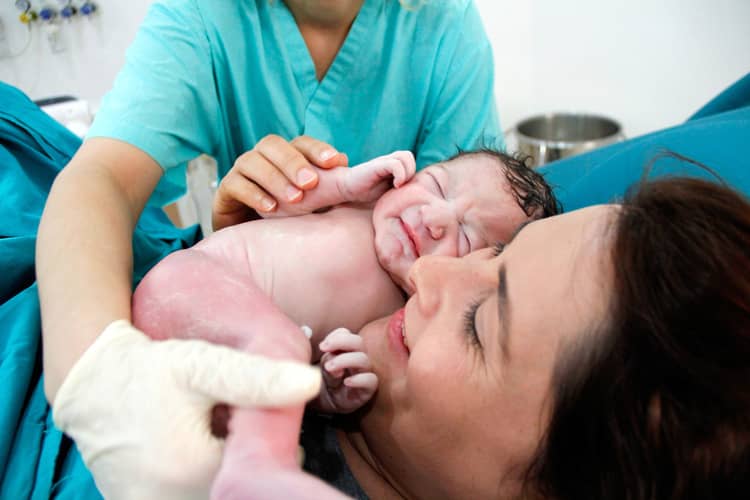

The course of bonding after childbirth
The entire bonding process is not complicated at all, on the contrary, it is a very natural thing. If the natural birth took place without complications and there are no risks, immediately after birth the baby is placed on the belly - mother's breast, skin to skin. A naked child should not be washed, but at most wiped dry with a towel so that the moist skin does not cool it. The reason is that there is amniotic fluid on the baby's body, which has the same taste and smell as the mother's nipples. After being placed on the mother's breast, the child is covered from above with a cloth (the child must not be wrapped in a blanket) in order to be warmed. From the bottom, it is the mother's body that warms the baby.
It is natural that the baby looks for the way to the breast after being placed on the body. The smell of nipples reminds him of the smell of amniotic fluid. Many children still latch on themselves during bonding. Such self-adherence already during the first contact is very beneficial for the further process of breastfeeding and also contributes in terms of supporting milk production in the mother.
All necessary examinations and measurements can wait for the bonding period. According to recommendations, the bonding time after childbirth should be at least 60-120 minutes, while the contact should not be interrupted. Some of the examinations can be performed by doctors directly during bonding. However, mother and child should be given peace.
Eye-to-eye contact between mother and child should be ensured. A newborn can only see well at a distance of about 20 to 30 cm. It is about the so-called mother's distance, the child can see the breast - the source of food during breastfeeding and perceive the mother's face. The mother should be able to have her head supported and be able to look at her baby. The child perceives the heartbeat and the mother's breathing (he also felt them in the belly), which calm him down. It is appropriate if the mother talks to the baby during bonding.
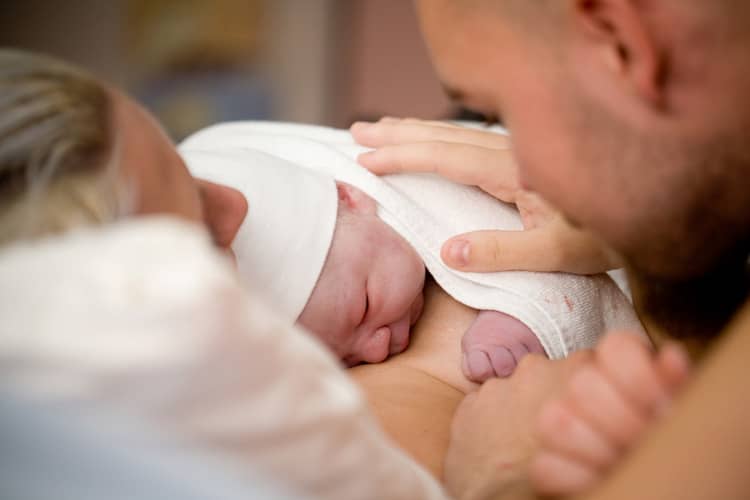

Benefits of bonding for newborn and mother
Scientific research, fact-based opinions of practicing doctors, as well as practical experiences of mothers point to the benefits of postpartum bonding. The skin-to-skin contact of the baby with the mother immediately after birth is considered a procedure in neonatology, the practice of which is important from the point of view of future processes. These take place in the child-mother relationship, but also in the next period of the child's personal development. The World Health Organization (WHO) also talks about the effects of bonding after childbirth, which, by analyzing research (2007) in this area, established the positive influence of this theory in practice. So what are the benefits of bonding for mother and child?
- A strong emotional bond is demonstrably built, which strengthens the mother's sense of pride and multiplies the love between mother and child. At the same time, the woman gains an experience that calms her down, she gains confidence and has the initiative to satisfy the child. The process is simultaneously soothing for the mother and the newborn.
- In a woman, endorphins, the hormone of happiness, are released in large quantities, which dull any pain after childbirth, and at the same time, the mother perceives that the child is safe, her stress is reduced and she is more relaxed.
- In the case of a newborn, by placing it on the mother's body, the so-called birth shock – the child suddenly has no support from the amniotic fluid or the abdominal walls. His mother's body, her touches, her scent and her persuasion will provide him with it.
- Research has shown an improvement in the child's postpartum adaptation to a new environment - the mother's body provides the child with immunological protection against pathogens that could threaten its immunity. During bonding, the child is placed skin-to-skin, and his body is populated by non-pathogenic bacteria that increase his immunological resistance (microflora is formed in the newborn).
- Research has shown that babies cradled immediately after birth are less crying and less prone to thermoregulation problems. Their production of stress hormones decreases. Their bodily functions, such as heartbeat and breathing, are also stabilized.
- Bonding can be proven to improve the success of long-term breastfeeding in mothers, and the self-attachment of the newborn during bonding significantly supports lactation in the breastfeeding woman. Midwives can also be helpful in this case. During breastfeeding, the hormone oxytocin is also released and it stimulates the production of milk.
- Direct contact between the mother and the child after birth has been proven to reduce the risk of postpartum depression and anxiety in mothers. Fears and suspicions about "why I don't have a child with me" are also eliminated.
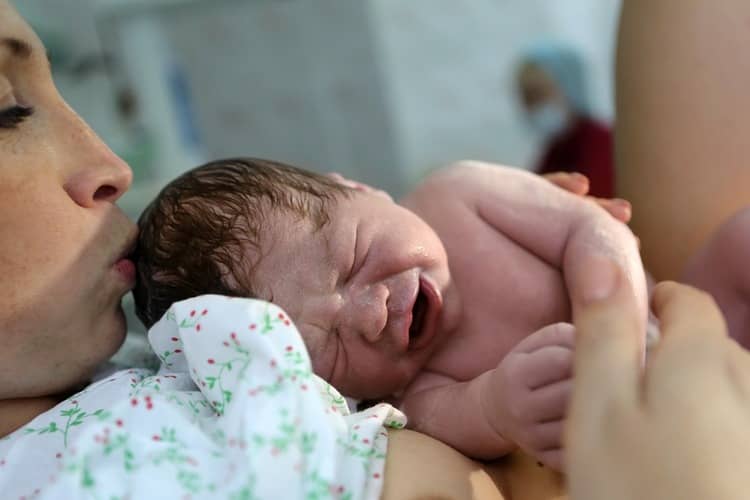

Bonding after caesarean section
Supporting bonding is very important, as shown by the above-mentioned results of research dealing with the effects of bonding on mother and child. In certain cases, bonding is also suitable for prematurely born - premature children. Of course, in circumstances where the child's health allows it. In the case of premature babies, the necessary examinations are first carried out in practice, and only shortly after the mother is allowed to put the baby skin-to-skin. And what about bonding after caesarean section?
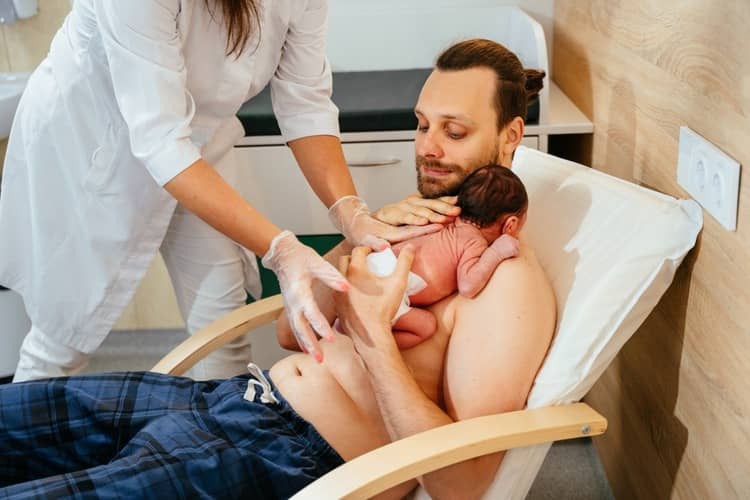
This is a very specific situation and it is generally not possible to say that it is impossible or inappropriate to deliver a baby after a caesarean section. A cesarean birth in the case of bonding may indicate a complication and it is up to the doctor and midwives to decide whether bonding will be possible or not. So it largely depends on other factors. Nevertheless, mothers do not have to worry that it will not be possible to build a bond with their baby. As soon as the state of health of the mother or the child allows it, the newborn is attached to the mother's breast. Although the following may seem bizarre in our conditions, if the father is present at the birth and for some reason bonding cannot take place with the mother, the father is the appropriate alternative.
Father bonding
The role of the father in this regard should not be neglected. In our conditions , the connection bonding and father is hardly known at all. Nevertheless, this connection is possible, literally. In the event that circumstances arise during or after childbirth that it is not possible for a woman to hold the baby close to her body for some reason, the father's chest is better than a blanket. A father's love for his child is again specific, but equally important. Although the father does not have as strong a bond with the child from the beginning as the mother, he can strengthen the bond by bonding. Rather, there are maternity hospitals abroad, but also in Slovakia, where it is possible to perform bonding on the father's body. Not only does the father represent the mother on a certain level and ensure a better process of adaptation to the new environment for the child, but they also strengthen their own bond, which will continue to develop.
Bonding in practice in Slovakia
The importance of bonding is known above all abroad. More and more pediatricians, gynecologists and obstetricians are talking about this theory in our conditions as well. Both UNICEF and WHO contain materials supporting bonding in their documents. These documents are supported by a lot of research. After all, the support for bonding - attaching a newborn after birth is included in the Journal of the Ministry of Health of the Slovak Republic in the Expert Guideline on the support and nutrition of infants and toddlers through breastfeeding. It clearly states that direct contact between mother and newborn immediately after birth should be allowed in all delivery rooms and maternity hospitals that carry the MBFHI - Mother and Baby Friendly Hospital Initiative label. We can label such facilities as "hospitals friendly to mothers and children", which may sound a little strange, since all maternity hospitals should be like that.
Research from 2016 dealt with the support of bonding after childbirth in Slovakia. His findings show that direct skin-to-skin contact (mother and child) - bonding was not allowed for 55.7% of mothers. 27.1% of mothers reported that the child was placed skin-to-skin between 1 and 5 minutes. Only 7.2% of female respondents stated that they had skin-to-skin contact with the child for 60 minutes or more after birth. According to established recommendations, immediate bonding should last at least 1 or 2 hours. In practice, it is also very common that the baby is taken away from the mother after birth. As many as 66.3% of respondents from the mentioned study stated that the child was brought to them within 30 minutes of birth, while it was washed and dressed, which cannot be considered as proper support for bonding.
Many respondents also said that the child was shown to them and then taken away (41.2%). Approximately 44.2 % of women reported that the child was placed skin-to-skin either on the chest, abdomen, or breast, which is a positive support for bonding. However, as research shows, mostly only for a very short time. It is therefore obvious that the support of bonding is only partially observed in Slovak hospitals and the implementation of real bonding is insufficient overall. This procedure is still considered a novelty by healthcare workers, and it does not have sufficient support and routine. In the practice of Slovak hospitals, it is still relatively common that the child is shown to the mother, then taken away, examined, washed and wrapped in a blanket. Subsequently, it is brought to the mother in the delivery room, roughly within 10 minutes of giving birth. This procedure cannot be considered as a direct support for bonding.
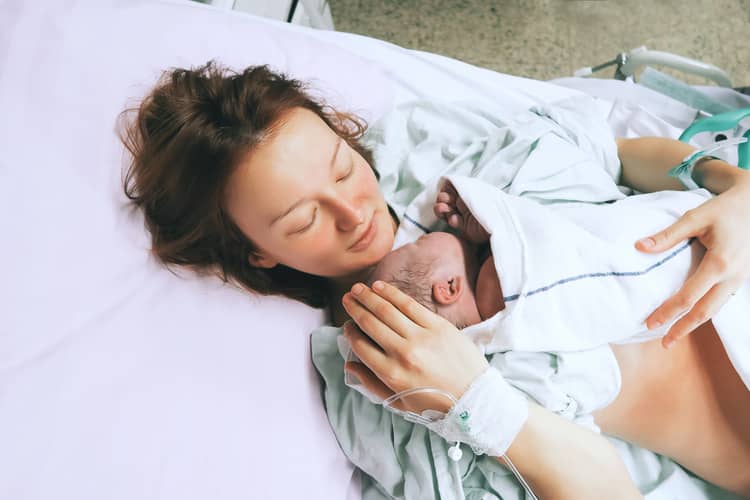

Bonding after childbirth - experiences
The experiences of mothers from Slovak hospitals confirm that many have not encountered bonding. The child was shown to them, taken away and brought back only after a series of examinations, washed and dressed. Some mothers say that their child was placed skin-to-skin, but only for a short time. Mothers talked about some maternity hospitals where bonding has been implemented for a long time, but it is still only about individual experiences. Mothers mainly consider calming down, stress relief, pain relief and a positive effect on their psyche after childbirth to be positive. The experience of one mother from a maternity ward in Germany also speaks of father bonding.
The most frequent questions - FAQ
Are you wondering what bonding is? What are its benefits in connection with a newborn? Why is bonding actually implemented? Is it possible for the mother to bond after a caesarean section? In our article, you will learn the most important things about this theory. If you have any questions, write us a comment and we will be happy to answer you as soon as possible. You can also consult with other readers. If you have experience with bonding, we would appreciate your opinions, stories, tips and recommendations. You can participate in the comments below the article.
What is bonding?
Is bonding possible after caesarean section?
Can the child's father undergo bonding?
Pridať komentár