Umbilical cord - when is it formed, how long is it, when to cut it after birth
The umbilical cord forms around the 4th week of pregnancy and connects the mother's placenta to the baby's navel. Until birth, it serves as a replacement for the baby's organs - it receives oxygenated blood and all the necessary nutrients (proteins, fats, vitamins...). The umbilical cord also serves to remove waste substances and deoxygenated blood. Despite the fact that the cord is only a few tens of centimeters long (the average length is 50 to 60 cm), it can provide everything necessary for the proper development of the child.
- The umbilical cord supplies the baby with blood and nutrients
- When does the umbilical cord form?
- The umbilical cord is twisted
- Both length and diameter may vary
- The beginning and end of the umbilical cord
- Can a wrapped umbilical cord be detected?
- He doesn't have nerves, but he can catch fire
- What does the navel look like after the umbilical cord falls off?
- Cutting the umbilical cord
- What is a two-vessel umbilical cord?
- Umbilical cord as a first toy
- Jelly with hyaluronic acid content
- Does cord blood help heal?
- The most frequent questions - FAQ
- Comments
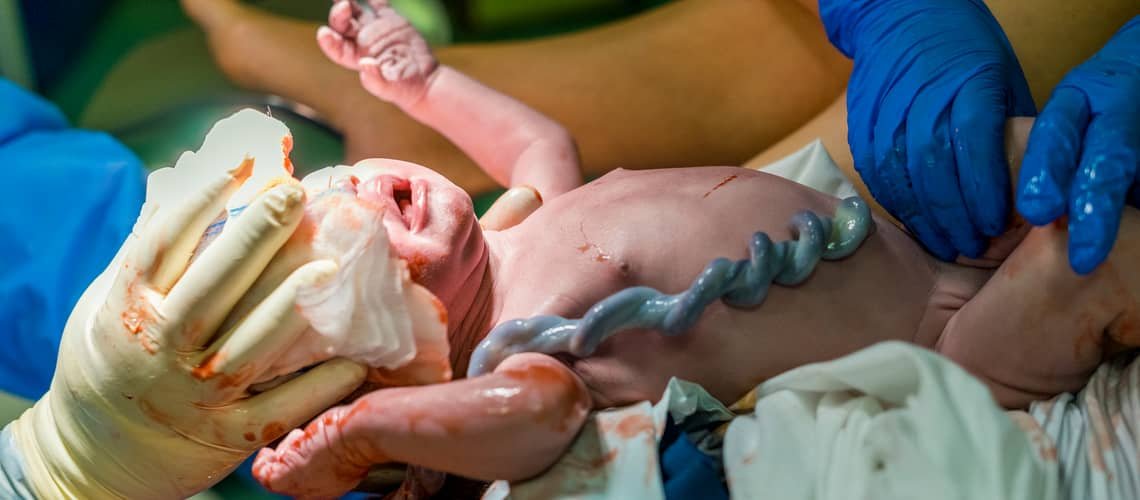
This physical and emotional bond between mother and fetus is often called the cord of life by poets. It is a bundle of blood vessels that develops in the early stages of embryonic development. The umbilical cord is a flexible, tubular anatomical structure covered with a jelly-like substance - Wharton's jelly/gelatin/jelly. We looked at some facts and interesting facts about this wonder of nature.
The umbilical cord supplies the baby with blood and nutrients
The umbilical cord is not an organ, but it represents the baby's organs. It acts as its lifeline, through which it receives nutrients and oxygenated blood and carries away deoxygenated blood and waste products. It consists of one vein and two arteries. Through the vein, the child receives the necessary substances for life, through the arteries unnecessary substances return to the placenta. About half a liter of blood flows through the umbilical cord in one minute.
When does the umbilical cord form?
Around the fourth week of pregnancy, the embryo develops a primitive navel with the bases of umbilical vessels within the so-called germinal shaft. The embryo already has yolk vessels and the layers of cells that will later develop into the skeleton, organs, skin or hair are noticeable. The embryo is as small as a poppy seed and its connection to the mother's blood circulation is underway. The foundations are formed for the formation of the placenta, the umbilical cord and the development of the baby's organs. The umbilical cord is fully developed at the end of the 2nd month, it grows until birth.
The umbilical cord is twisted
Since the umbilical cord grows very quickly, it twists into a spiral shape, which prevents the umbilical cord from knotting. Twisting to the left prevails over twisting to the right, it is a ratio of 7 to 1. Only in approximately 5%, twisting does not occur at all.
Both length and diameter may vary
In full-term newborns, the average length of the umbilical cord is 50 to 60 cm, but it can reach 30 (short umbilical cord) to 130 cm (very long umbilical cord). A longer cord tends to be typical for more active babies (especially in the 2nd trimester). Neither a short nor a long cord is an advantage. In the first case, childbirth can be complicated, in the second case, the child's life can be entangled and endangered. The diameter of the umbilical cord is usually 1 to 2 cm.
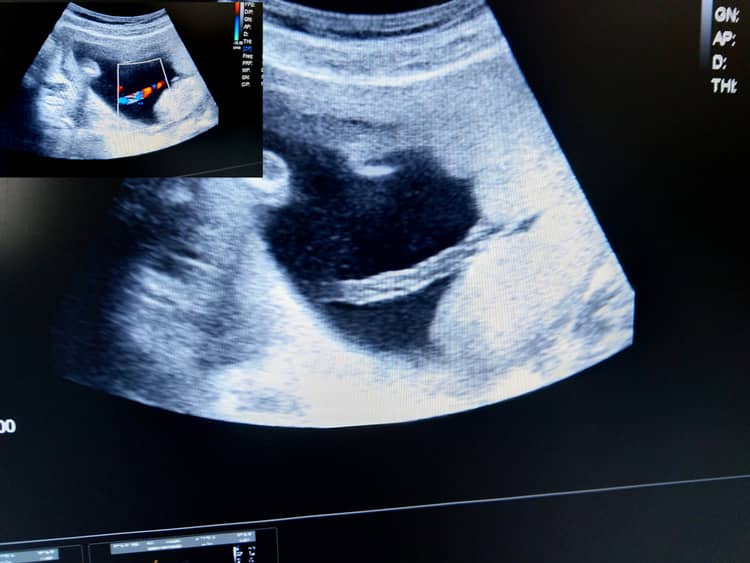
The beginning and end of the umbilical cord
One end of the umbilical cord is attached to the placenta, the other is connected to the fetus in the navel area. The umbilical cord attaches to the placenta most often in the middle, but it can also be attached to the edges or membranes. The placental membrane ensures that the mother's blood does not mix with the baby's blood and that there is no strong immune reaction (breakdown of the baby's blood cells).
Can a wrapped umbilical cord be detected?
Approximately one third of children are born with a tangled cord (often around the neck). This fact usually does not mean problems, they occur if the umbilical cord is very tight and the proper oxygenation of the baby is compromised. A coiled cord, threatening the baby's life, can be identified by monitoring the baby's heart activity during delivery.
He doesn't have nerves, but he can catch fire
There are no nerves inside or on the cover of the umbilical cord, therefore neither the mother nor the child can feel pain during pregnancy, when it is tied and cut. The drying and shedding of the growth after childbirth is also painless. However, this does not mean that infection cannot occur. The protrusion should not be moved or removed by force, it will fall off naturally after some time. It must be handled carefully and always only with clean hands. Its surroundings need to be regularly disinfected.
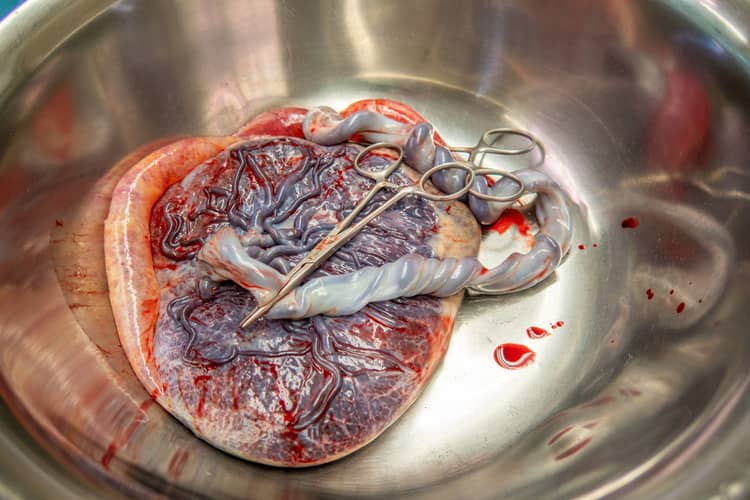
What does the navel look like after the umbilical cord falls off?
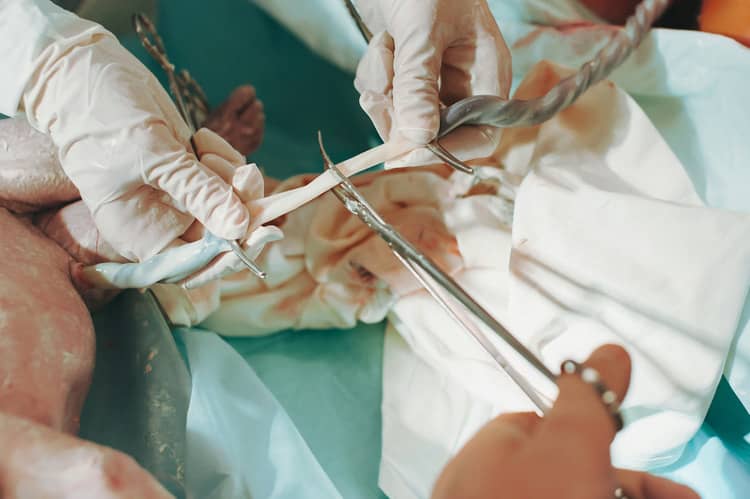
The answer to this question is not clear-cut, because the final appearance of the navel has nothing to do with how the umbilical cord was cut. After birth, the umbilical cord is clamped with two plastic clamps (or surgical thread) - the first is at a distance of 2-4 cm from the newborn's abdomen, the second is placed near the placenta, i.e. at the end of the umbilical cord. It is cut behind the first clamp and the stump is gradually allowed to dry. The rest of the umbilical cord gradually turns black and shrinks. It will fall off within about 15 days, leaving behind a "scar" - navel.
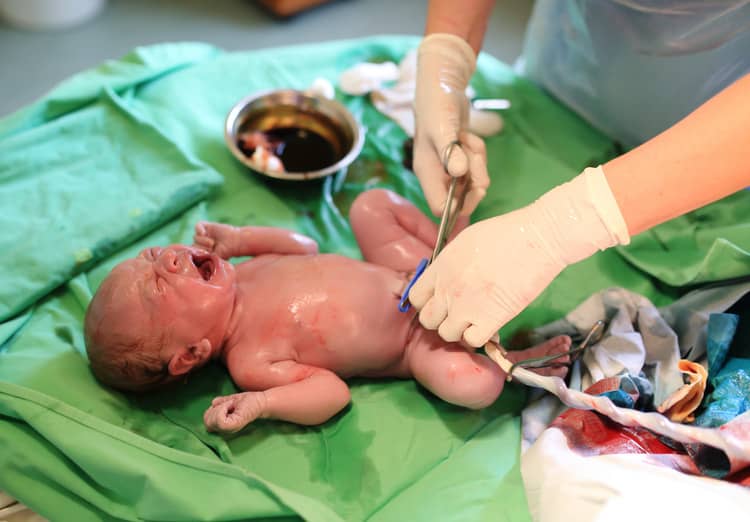
Cutting the umbilical cord
The umbilical cord can be cut immediately after birth, but also after pulsation. Until recently, tying and cutting the umbilical cord was performed a few seconds after birth, according to recent research, it is more appropriate to cut it at least 30-60 seconds after birth. For some time after birth, blood transport occurs, thanks to which not only the volume of blood in the child's body increases, but also iron reserves.
Lotus birth is practiced in some cultures. In this case, the umbilical cord is not cut, it remains connected to the baby until it falls off. The child is therefore connected to the placenta for several days after birth.
What is a two-vessel umbilical cord?
It is a congenital developmental defect/anomaly of the umbilical cord. Normally, the umbilical cord has two arteries (arteries) and one vein (vein). The reason why only one artery developed is not clear. The anomaly can be detected using USG (ultrasonography) examination. Many babies with a two-vessel umbilical cord are born perfectly healthy, despite the higher risk of congenital heart defects. After birth, in the case of this anomaly, it is recommended to carry out a detailed ultrasound examination focused on the newborn's heart.
Umbilical cord as a first toy
Babies are very curious and it shows even in the womb. The child is interested in his surroundings and explores them. The umbilical cord serves as his first toy to make the time spent in the tummy more pleasant. The baby pulls, squeezes, licks and clings to it.
Jelly with hyaluronic acid content
Inside the umbilical cord, there is a gelatinous substance that protects the vein and artery from kinking or compression. Wharton's jelly contains hyaluronic acid, which attracts water and hydrates, can bind up to 1000 times its weight. The surface of the umbilical cord is covered with a protective membrane (amnion). The umbilical cord is so strong and durable that it can withstand a weight of 6 kg.
Does cord blood help heal?
The blood in the umbilical cord contains hematopoietic stem cells, which could potentially be helpful in the treatment of some diseases. You can have blood taken during childbirth after cutting the umbilical cord and have it stored for your own use (for the child from whom it was taken, or for a sibling) or donated.
Various clinical studies are investigating the effectiveness of umbilical cord blood, but the results of its action have not yet been 100 percent confirmed. Even with a bone marrow transplant, cord blood is one of the few other options. Because the cells are less mature, its effects are weaker.
The most frequent questions - FAQ
The umbilical cord is of great importance for both mother and child. Through it, the child receives fresh blood and the necessary nutrients, removes waste substances and deoxygenated blood, and protects against the mixing of the mother's and child's blood. Are you curious about the umbilical cord? Do you want to ask something else about the umbilical cord? Join the discussion and tell us what interests you in the comments.
How does the umbilical cord work?
Is cutting the umbilical cord painful for the child or the mother?
What is the recommended treatment for the umbilical cord after cutting?
Umbilical cord around the neck - what are the consequences?
Pridať komentár